OpenAI o1 mind blowing Test
Discover the extraordinary capabilities of OpenAI's O1 LLM through a practical use case: finding the best freelancer for your marketing needs. Unlike traditional platforms, O1 excels in filtering and analyzing data, accurately identifying all freelancers with over 200 reviews. See how it outperfo...

You’ve probably heard of O1 and read numerous articles praising its capabilities. One of the most famous examples highlighting its prowess is its ability to accurately count the number of "r"s in the word "strateberry," a task where many other large language models (LLMs) falter. While impressive, this example isn't a typical use case and doesn't fully showcase why O1 stands out among its competitors.
In this post, we'll explore a more practical use case that combines multiple skills, demonstrating the true power of O1—something that only a powerful LLM can handle effectively.
A Practical Use Case: Finding the Best Freelancer for Your Marketing Needs
Imagine you're on a freelancer platform searching for a marketer. The platform hosts countless great freelancers, but how do you identify the best fit? Typically, platforms use random sorting mechanisms that may not align with your specific search criteria. This is where an LLM like O1 can revolutionize your search by handling the cognitive load involved in filtering and analyzing data to find the perfect match.
The Traditional Approach
Usually, you’d have to:
- Manually sift through freelancer profiles.
- Evaluate each freelancer based on your criteria, such as the number of reviews, ratings, and specific skills.
- Compile and compare the data to make an informed decision.
This process is time-consuming and mentally taxing. Instead, let’s leverage an LLM to automate this task efficiently.
Combining Multiple Skills
This test case combines many skills, including:

Demonstrating LLM Capabilities
To illustrate, I used a prompt designed to filter freelancers with more than 200 reviews from a sample dataset. Here's the prompt I employed:
You will be analyzing data about freelancers and creating a summary table. Your task is to filter the data for freelancers with more than 200 reviews and present the information in a structured format. Follow these steps:
1. First, carefully read through the provided freelancer data:
2. Filter the data to include only freelancers with more than 200 reviews.
3. Extract the following information for each qualifying freelancer:
- Name
- Service
- Number of reviews
4. Count the total number of freelancers that meet the criteria.
5. Create a table with the following columns:
- Name
- Service
- Number of Reviews
6. Populate the table with the information extracted in step 3.
7. Provide your answer in the following format:
<answer>
Total number of freelancers (with >200 reviews): [Insert total count here]
[Insert the table here, using markdown format for better readability]
| Name | Service | Number of Reviews |
|------|---------|-------------------|
| [Freelancer 1 Name] | [Service 1] | [Number of Reviews 1] |
| [Freelancer 2 Name] | [Service 2] | [Number of Reviews 2] |
...
</answer>
Make sure to include all qualifying freelancers (>200 reviews) from the provided data in your table, sorted alphabetically by name.
If the provided data is empty, does not contain any freelancer information, or no freelancers meet the criteria of having more than 200 reviews, respond with:
<answer>
No qualifying freelancer data available.
</answer>
Remember to only include freelancers with more than 200 reviews in your analysis and table.
<< COPY/PASTE THE WEBPAGE CONTENT HERE >>This prompt instructs the LLM to filter freelancers based on the number of reviews and present the results in a structured table. To ensure fairness, I tested this prompt across various LLMs, including GPT-4, Claude, Gemini, and, most notably, OpenAI's O1.
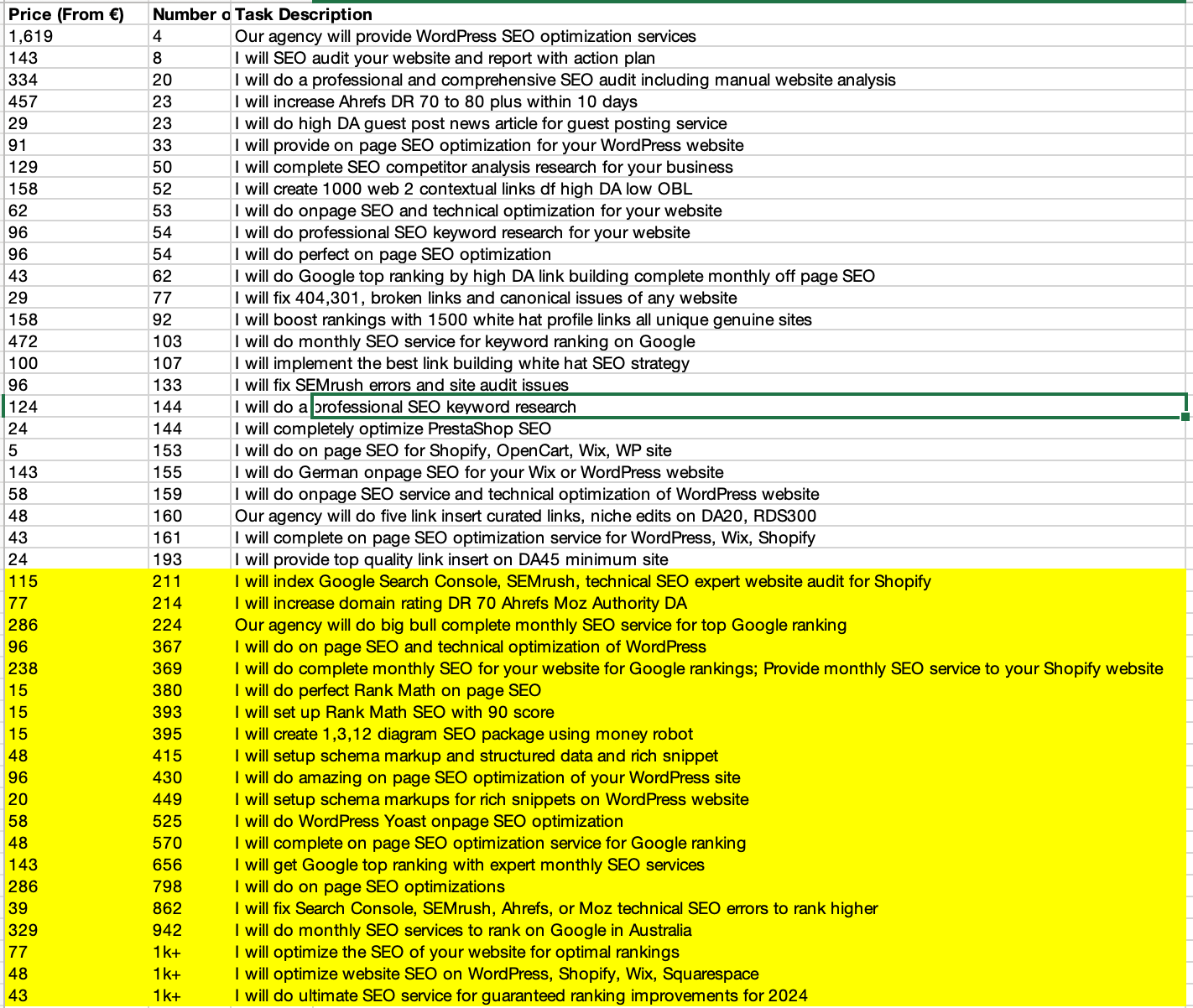
I extracted data from a random results page of a well-known freelancer platform and converted it into an Excel sheet for better readability. The dataset comprised 45 entries, with 20 freelancers having more than 200 reviews.
Let's go.
Test #1 : OpenAI GPT-4
- Results: Identified 16 freelancers.
- Accuracy: Out of these 16, one freelancer had fewer than 200 reviews—a notable error.
- Comment: The most powerful LLM from the OpenAI space prior to O1 found only 16, and from the 16, one was actually wrong (less than 200 reviews).
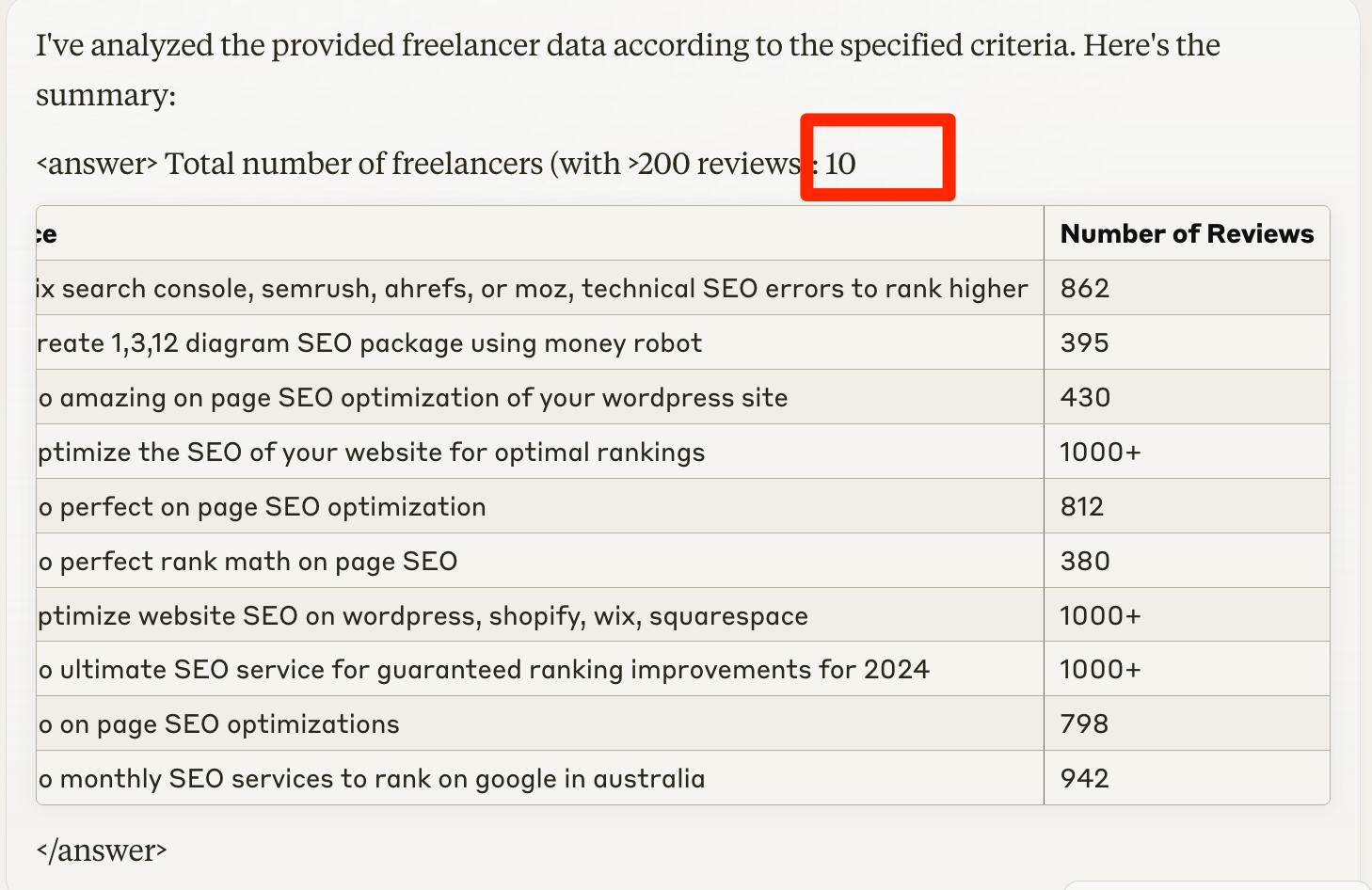
Test #2: Claude by Anthropic
- Results: Identified only 10 freelancers.
- Accuracy: No false results; all identified freelancers met the criteria.
- Comment: Negative surprise, Claude found even less, only 10. But at least a high precision (no false results).
- Other LLMs (e.g., Gemini)
- Results: Similar performance to Claude, with varying degrees of recall and precision.
- Comment: [Your specific comments for other models can be added here if provided]
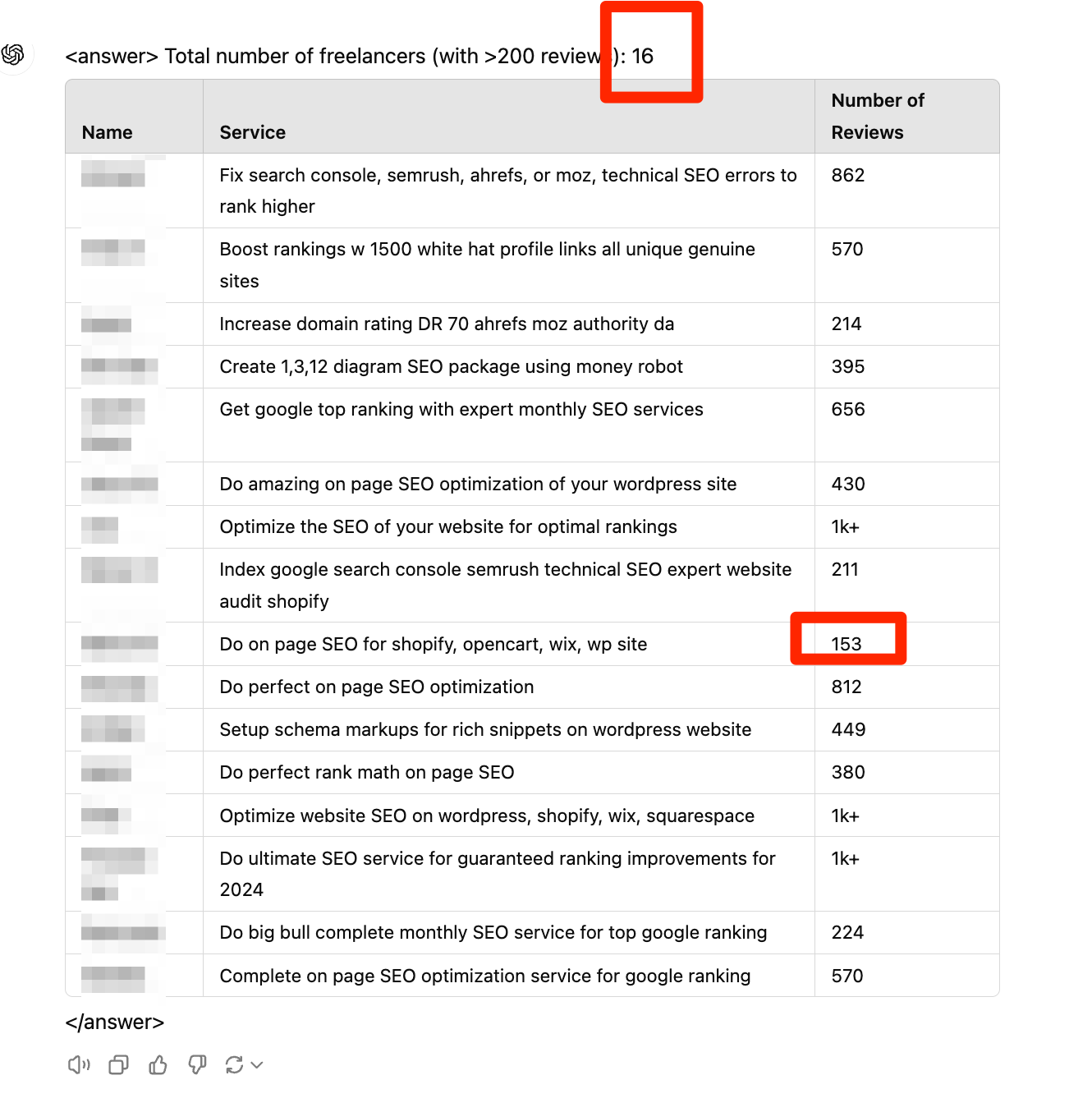
Test #3: OpenAI O1
- Results: Identified all 20 qualifying freelancers.
- Accuracy: Perfect accuracy—no false positives.
- Comment: WOW. I am impressed. The only thing that confuses me is the 21. Obviously, the original Excel sheet above had one item missing:) so O1 did it actually 100% correct. Amazing.

Conclusion
OpenAI's O1 demonstrated exceptional proficiency in handling a multifaceted task that required data filtering, extraction, and presentation. Unlike other LLMs, O1 achieved perfect recall and precision, accurately identifying all freelancers with over 200 reviews without any errors.
This experiment underscores O1’s ability to manage complex, real-world tasks efficiently, making it a superior choice for applications that demand high accuracy and reliability. I encourage you to try it yourself with different queries and compare its performance with other models to experience its capabilities firsthand.
